In the realm of industrial internet of things (IoT), the question of whether RJ45 and RS232 are the same often arises. While both are communication interfaces, they are significantly different in their design, function, and applications. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective data transmission and network connectivity in industrial settings.
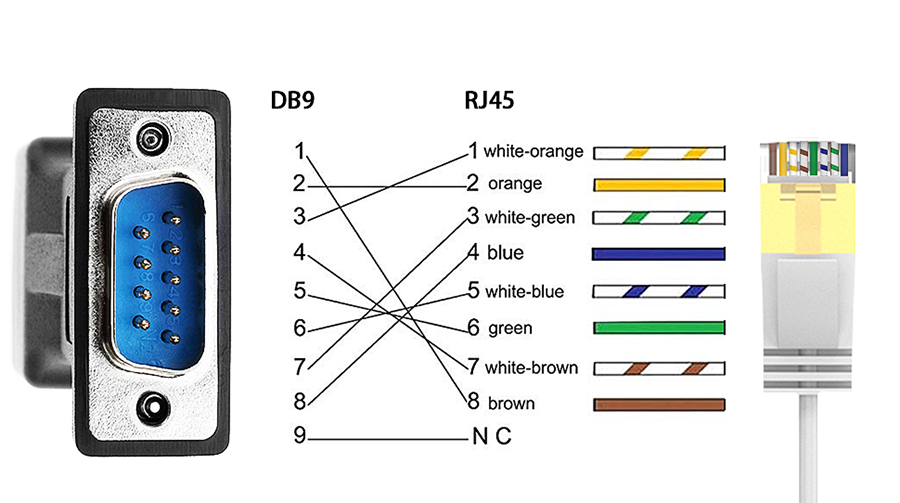
RJ45 is a type of connector commonly used in Ethernet networking. It's the physical interface that allows devices to connect to a local area network (LAN) or the internet. RJ45 connectors are typically found on the ends of Ethernet cables and are used to plug into corresponding ports on network devices such as routers, switches, and computers. The RJ45 connector features eight pins arranged in a specific pattern, allowing for high-speed data transmission over long distances.
RS232, on the other hand, is a serial communication standard that was developed in the 1960s. It defines the electrical and mechanical characteristics of data transmission between devices. RS232 cables typically have a male connector at one end and a female connector at the other, allowing for point-to-point communication between two devices. RS232 is commonly used in older industrial equipment and systems that require low-speed data transmission over short distances.
The primary difference between RJ45 and RS232 lies in their application and capabilities. RJ45 is designed for high-speed network communication, enabling devices to connect to a larger network or the internet. It supports much higher data rates than RS232, making it suitable for industrial IoT applications that require real-time data exchange and high-bandwidth communication.
In contrast, RS232 is limited to slower data transmission speeds and shorter distances. It's primarily used in legacy equipment and systems that don't require high-speed network connectivity. RS232 is also more susceptible to noise and interference, which can affect data integrity.
Another significant difference is the physical layout of the connectors. RJ45 connectors have a specific pin arrangement that aligns with the pins in the corresponding port on a network device. RS232 connectors, on the other hand, typically have a male and female configuration that allows for a direct connection between two devices.
When selecting the appropriate communication interface for an industrial IoT application, it's crucial to consider the specific requirements of the system. If high-speed network connectivity and real-time data exchange are essential, RJ45 is the more suitable choice. However, if the application involves legacy equipment or systems that require simple point-to-point communication, RS232 may be a more cost-effective solution.
RJ45 and RS232 are not the same. RJ45 is a connector used in Ethernet networking for high-speed data transmission over longer distances, while RS232 is a serial communication standard primarily used in legacy equipment for low-speed, short-distance communication. Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed decisions about the communication interfaces used in industrial IoT applications.
In the realm of industrial internet of things (IoT), the choice of communication interfaces and cables plays a pivotal role in ensuring reliable and efficient data transmission. RS232, a serial communication protocol, has been around for decades and is still widely used in various industrial applications. However, when it comes to using RS232 over Category 6 (Cat 6) cables, questions often arise regarding the transmission distance.
RS232 is a serial communication standard that was initially designed for data transmission over relatively short distances. It utilizes a single pair of wires for both data transmission and reception, and its speed is typically measured in baud rates. Common baud rates for RS232 include 9600, 19200, and 38400, among others. While RS232 is known for its simplicity and direct point-to-point connection, it has inherent limitations in terms of speed and transmission distance.
Category 6 cable, commonly known as Cat 6, is a type of network cable designed for high-speed data transmission over longer distances. It supports Gigabit Ethernet speeds and is widely used in modern computer networks and industrial IoT systems. Cat 6 cables are characterized by their excellent performance and reliability, making them a popular choice for industrial applications that require robust network connectivity.
When considering the use of RS232 over Cat 6 cables, it's important to understand that these two technologies are not naturally compatible. RS232 was designed for specific types of cables and connectors, while Cat 6 cables are optimized for Ethernet and other networking protocols. Therefore, using RS232 over Cat 6 cables is not a straightforward task.
The transmission distance of RS232 over Cat 6 cables is limited by several factors. Firstly, the inherent limitations of RS232 itself, such as its relatively low baud rates and single-wire pair design, restrict the maximum distance over which data can be transmitted reliably. Secondly, the impedance mismatch between RS232 and Cat 6 cables can lead to signal degradation and attenuation over longer distances.
While there is no specific, fixed limit on the transmission distance of RS232 over Cat 6 cables, it is generally recommended to keep the distance as short as possible to ensure reliable data transmission. In practice, the maximum transmission distance may vary depending on the specific baud rate used, the quality of the cables and connectors, and the presence of any potential sources of interference.
If you need to transmit data over longer distances in an industrial IoT system, it may be more practical to consider using Ethernet or other networking protocols instead of RS232. Ethernet, for example, offers significantly higher speeds and better bandwidth utilization over Cat 6 cables, making it a more suitable choice for modern industrial applications.
However, if you must use RS232 due to legacy equipment or specific requirements, you may need to employ additional measures to extend the transmission distance. This could include the use of signal repeaters or converters that can regenerate or convert the RS232 signal over longer distances. It's important to note that such solutions may introduce additional complexity and cost to your system.
The transmission distance of RS232 over Category 6 cables is limited by the inherent characteristics of RS232 and the impedance mismatch between the two technologies. While there is no fixed limit, it is generally advisable to keep the distance as short as possible to ensure reliable data transmission. For longer-distance communication in industrial IoT systems, Ethernet or other networking protocols are more suitable choices. Understanding these limitations and considering alternative solutions will help you design and deploy robust and reliable industrial IoT systems.
In the evolving landscape of industrial internet of things (IoT), it's natural to question the relevance and continued usage of older communication standards like RS232. This serial communication protocol has been around for decades, playing a pivotal role in various industrial applications. But with the advent of newer, faster, and more efficient technologies, does RS232 still have a place in today's industrial IoT ecosystems?
RS232, originally developed in the 1960s, revolutionized data communication in its early days. It provided a simple and reliable means of connecting devices for data exchange, often over relatively short distances. Its widespread adoption across industries was due to its straightforward implementation and low cost. RS232 cables were commonly seen in various industrial settings, connecting devices such as modems, printers, and computers.
Despite the advancements in communication technologies, RS232 cables are still in use in some industrial settings. This is primarily due to the large installed base of legacy equipment that relies on RS232 for communication. Many older industrial machines and systems were designed with RS232 interfaces, and replacing them with newer technologies can be costly and impractical.
Moreover, in some specific applications, RS232 may still offer advantages over newer protocols. For instance, in scenarios where simple point-to-point communication is required, and speed is not a critical factor, RS232 can provide a cost-effective solution. Additionally, it can be useful in environments where electromagnetic interference (EMI) is a concern, as RS232 cables are less susceptible to EMI than some other types of cables.
However, it's important to acknowledge that RS232 faces several challenges in today's industrial IoT environment. Its relatively low data transmission speeds and limited cable lengths can be limiting factors in modern industrial applications that require high-speed data exchange over longer distances. Furthermore, RS232 cables are susceptible to noise and interference, which can affect data integrity.
As industrial IoT systems become more complex and demanding, newer communication technologies have emerged to address the limitations of RS232. Technologies like USB, Ethernet, and various wireless protocols offer higher speeds, greater reliability, and longer transmission distances. These newer technologies are increasingly being adopted in industrial settings, gradually replacing RS232 in many applications.
While RS232 cables are still in use in some industrial settings due to legacy equipment and specific application requirements, their relevance is waning as newer, more advanced technologies take over. As industrial IoT systems continue to evolve, it's likely that RS232 will gradually be phased out, replaced by more modern and efficient communication solutions. However, for the foreseeable future, RS232 will remain a familiar and trusted standard in certain industrial applications where its simplicity and cost-effectiveness still hold value.